Docstrings in twinBASIC
twinBASIC takes a page out of the RubberduckVBA book, using code comment "annotations" to generate real-time, IntelliSense-integrated documentation.

To learn more about twinBASIC, join me at this year's virtual Access DevCon where I will be presenting this exciting new project from vbWatchdog creator, Wayne Phillips.
Rubberduck-like annotation syntax
Fans of the Rubberduck VBA project will be happy to hear that at least some of the annotation syntax from that project is built in to twinBASIC.
Here's a sample of the @Description annotation in use in twinBASIC:
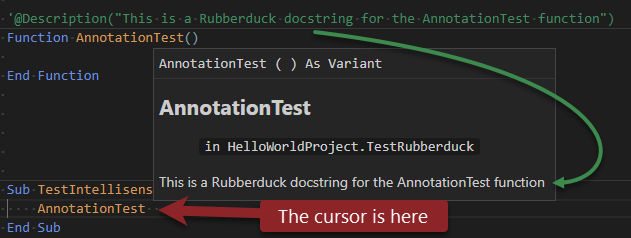
Other annotations
Some annotations, like @Folder, are unnecessary in twinBASIC.
Others, like @VariableDescription, can't be tested yet because they depend on features not available in the twinBASIC preview (such as module-level and global variables).
Yet others, like @ModuleDescription, I simply wasn't able to get working in twinBASIC (I don't know if that's on me or if it's not supported). UPDATE (4/14/21): There's no need for a standalone @ModuleDescription annotation in twinBASIC. The @Description annotation can be written above the Class Xxxx or Module Xxxx lines to provide inline documentation that applies to the respective class or module:
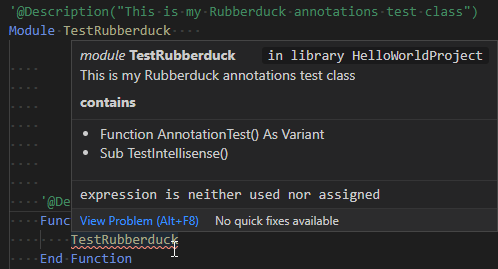
Finally, there are a handful of annotations–like @DefaultMember and @EnumeratorMember–that make it easier to manage hidden attributes that are not directly accessible from the VBA editor. I'm not sure how twinBASIC plans to handle those attributes.
UPDATE (4/14/21): Show proper usage for class- and module-level docstrings.
